 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe rate of the reaction,
2NO + Cl2 → 2NOCl is given by the rate equation, rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]
The value of the rate constant can be increased by
increasing the temperature
increasing the concentration of NO
increasing the concentration of the Cl2
increasing the concentration of the Cl2
Half-life period of a first order reaction is 1386 s. The specific rate constant of the reaction is
5.0 x 10-3s-1
0.5 x 10-2 s-1
0.5 x 10-3 s-1
0.5 x 10-3 s-1
For the reaction, A+B → Products, it is observed that
1) On doubling the initial concentration of A only, the rate of reaction is also doubled and
2) On doubling the initial concentrations of both A and B , there is a change by a factor of 8 in the rate of the reaction.
The rate of this reaction is, given by
rate = k [A]2[B]
rate = k[A][B]2
rate = k[A]2[B]2
rate = k[A]2[B]2
For the reaction, N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3, If 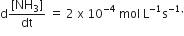 the value of
the value of 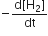 would be
would be
3 x 10-4 mol L-1 s-1
4 x 10-4 mol L-1s-1
6 x 10-4 mol L-1s-1
6 x 10-4 mol L-1s-1
In the reaction,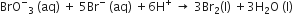
The rate of appearance of bromine (Br)2 is related to rate of disappearnace of bromide ions as following
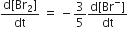

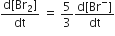
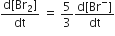
The rate constant k1 and k2 for two different reactions are 1016. e-2000/T and 1015.e-1000/T respectively. The temperature at which k1 = k2
1000 K
2000/2.303 K
2000 K
2000 K
The bromination of acetone cytosine and guanine solution is represented by this equation.
CH3COCH3 (aq) + Br2 (aq) →CH3COCH2Br (aq) + H+ (aq) + Br- (aq)
These kinetic data were obtained for given reaction concentrations.
|
Initial Concentrations, M
|
||
| [CH3COOH] | [Br2] | [H+] |
| 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.20 |
Rate = k[CH3COCH3][H+]
Rate = k[CH=COCH3][Br2]
Rate = k [CH3COCH3][Br2][H+]
Rate = k [CH3COCH3][Br2][H+]
The reaction of hydrogen and iodine monochloride is given as:
H2 (g) + 2ICl (g) → 2 HCl (g) + I2 (g)
This reaction is of first order with respect to H2 (g) and ICI (g), following mechanisms were proposed:
Mechanism A:
H2 (g) + 2 ICl (g) → 2 HCl (g) + I2 (g)
Mechanism B:
H2 (g) + ICl (g) →HCl (g) + HI (g) ;slow
HI (g) + ICl (g) → HCl (g) + I2 (g); fast
Which of the above mechanism (s) can be consistent with the given information about the reaction?
B only
A and B both
Neither A nor B
Neither A nor B
B.
A and B both
The rate of reaction always depends on slow reaction.
H2 (g) + ICl (g) →HCl (g) + HI (g) is a first order reaction respect to H2 and I2 can measure with the help of both mechanism A and B.
In a first order reaction A →B, if k israte constant and initial concentration of the reactant A is 0.5 A M then the half -life is :
0.693/0.5 k
log2/k
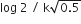
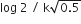
If 60% of a first order reaction was completed in 60 min, 50% of the same reaction would be completed in approximately:
50 min
45 min
60 min
60 min
