 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe chemical reaction 2O3 3O2 proceeds as :
(I) O3 O2 + O (fast)
(II) O + O3 2O2 (slow)
The rate expression should be :
r = k[O3]2
r = k[O3]2 [O2]-1
r = k[O3] [O2]
None of these
For a 1st order reaction if concentration is doubled then rate of reaction becomes
doubles
half
four times
remains same
The first order rate constant for dissociation of N2O5 is 6.2 x 10-4 s-1 .The half-life period (in s) of this dissociation will be :
1117.7
111.7
223.4
160.9
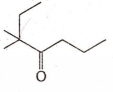
The IUPAC name of the compound :
 is :
is :
2 - ethyl - 2 - methyl - 3 - hexanone
5 - ethyl - 5 - methyl - 4 - hexanone
5 , 5 - dimethyl - 4 - heptanone
3 , 3 - dimethyl - 4 - heptanone
D.
3 , 3 - dimethyl - 4 - heptanone
 can be written as
can be written as
![]()
3 , 3 - dimethyl - 4 - heptanone
The gas phase reaction of nitric oxide and bromine yields nitrosyl bromide :
2NO (g) + Br2 (g) 2NOBr (g)
The rate law is rate = k[NO]2[Br2]
The overall reaction order is :
1
2
3
4
For a reaction XY,the graph ofthe product concentration (x) versus time (t) came out to be a straight line passing through the origin. Hence the graph of and time would be
straight line with a negative slope and an intercept on y-axis
straight line with a positive slope and an intercept on y-axis
a straight line parallel to x-axis
a hyperbola.
If 8. 0 g of a radioactive isotope has a half-life of 10 yr .The half-life of 2.0 g of the same substance is :
2.5 yr
5 yr
20 yr
lO yr
Which one of the following is a second order reaction ?
H2 + Br2 2HBr
NH4NO3 N2 + 3H2O
H2 + Cl2 2HCl
CH3COOCH3 + NaOH CH3COONa + CH3OH
Assertion : Two different reactions can never have same rate of reaction.
Reason : Rate of reaction always depends only on frequency of collision and Arrhenius factor.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion : Rate of reaction of alkyl halide in Williamson's synthesis reaction is 1°RX > 2°RX > 3RX.
Reason : It is a type of bimolecular substitution reaction (SN2).
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
