 Long Answer Type
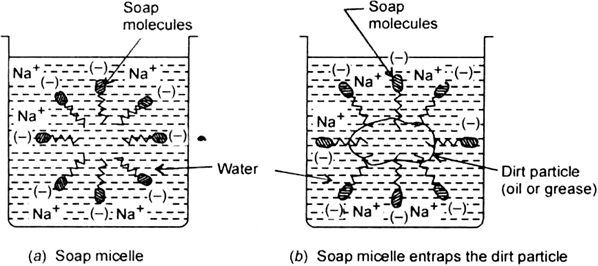
Long Answer TypeExplain the cleansing action of soaps.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeMade an example and functon of the following:
(i) Tranquilizers
(li) Wide spectrum antibiotics
Sulpha drugs work like antibiotics but they are not antibiotics. Is this a valid statement and why? Give one example of sulpha drugs and antibiotics.
What is meant by chemotherapy? Write the chemical name of aspirin. What is it used for?
Define spectrum. Give two examples of each of:
(a) narrow-spectrum antibiotics
(b) broad-spectrum antibiotics.
