 One Word Answers
One Word Answers Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeList various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds, giving an example of each.
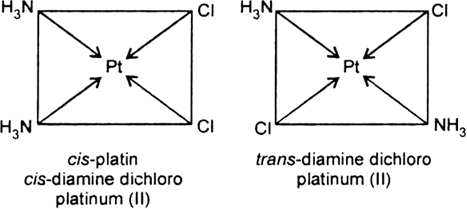
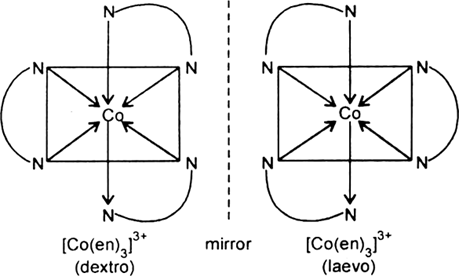
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow many geometrical isomers are possible in the following coordination entities?
[Cr(C2O4)3]3–
How many geometrical isomers are possible in the following coordination entities?
[Co(NH3)3Cl3].
