 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDraw figure to show splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field.
Crystal field effects in octahedral coordination entities:
(i) Let us assume that the six ligands are positioned symmetrically along the cartesian axes, with metal atom at the origin. As the ligands approach first there is an increase in energy of d-orbitals relative to that of the free ion just as would be the case in a spherical field.
(ii) The orbitals lying along the axes (dz2 , and dx2– y2) get repelled more strongly than d xy’, d yz. and d zx orbitals which have lobes directed between the axes.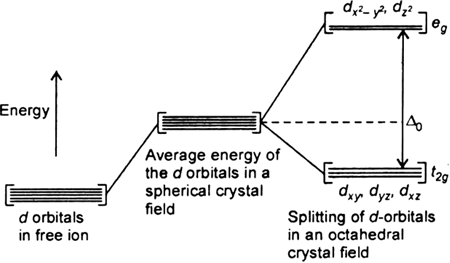
Fig. d-orbital splitting in an octahedral crystal field.
The dz2 , and dx2– y2 orbitals get raised in energy and dxy, dyz, dxz orbitals are lowered in energy relative to the average energy in the spherical crystal field.
Thus, the degenerate set of d-orbitals get split into two sets: the lower energy orbitals set t2g and the higher field energy orbitals eg set. The energy is separated by Δ0.
What is spectrochemical series? Explain the difference between a weak field ligand and a strong field ligand.
