 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeUsing valency bond approach predict the shape and magnetism (paramagnetic or diamagnetic) of [Ni(CN)4]–.
Explain the following terms: (i) Inner orbital complex and (ii) outer orbital complex.
Deduce the structures of [NiCl4]2– and [Ni(CN)4]2– considering the hybridization of the metal ion. Calculate the magnetic moment (spin only) of the species.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe carbonyls are formed by most of the transition metals. These carbonyls have simple, well defined structures.
The metal-carbon bond in metal carbonyls
possess both σ and π character. The M–C σ bond is formed by the donation of lone pair of electrons on the carbonyl carbon into a vacant orbital of the metal. The M–C π bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electrons from a filled d orbital of metal into the vacant antibonding π* orbital of carbon monoxide. The metal to ligand bonding creates a synergic effect which strengthens the bond between CO and the metal.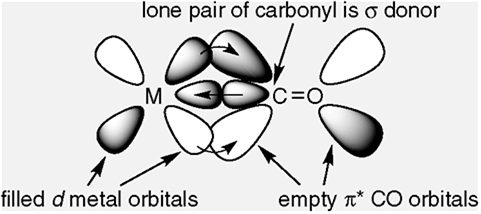
Illustrate with an example each of the following terms: (i) Ionization isomerism, (ii) coordination isomerism, (iii) Linkage isomerism, (iv) Geometrical isomerism (v) Optical isomerism.
Draw the isomers of each of the following:
(i) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] (ii) [PtCl3Br3]2–
(ii) [Co(NH3)4Cl2] (iv) [Co(en)2Cl2]+.
