 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe pH of a 0.02 M NH4Cl solution will be: [ given Kb(NH4OH) = 10-5 and log 2= 0.301]
5.35
2.65
4.65
4.35
For the reaction, 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g), ΔH= -57. 2kJ mol-1 and Kc = 1.7 × 106. Which of the following statement is INCORRECT ?
The equilibrium constant is large suggestive of reaction going to completion and so no catalyst is required
The equilibrium constant decreases as the temperature increases.
The equilibrium will shift in forward direction as the pressure increase
Volume will not affect the equilibrium constant
The addition of a catalyst during a chemical reaction alters which of the following quantities ?
Internal energy
Enthalpy
Activation energy
Activation energy
Which one of the following characteristics is associated with adsorption?
ΔG, ΔH and ΔS all are negative
ΔG and ΔH are negative but ΔS is positive
ΔG and ΔS are negative but ΔH is positive
ΔG and ΔS are negative but ΔH is positive
MY and NY3, two nearly insoluble salts. have the same Ksp values of 6.2 x 10-13 at room temperature. Which statement would be true in regard to MY and NY3 ?
The molar solubility of MY in water is less than that of NY3
The salts MY and NY3 are more soluble in 0.5 M KY than in pure water
The addition of the Salt of KY to the solution of MY and NY3 will have no effect on their solubilities.
The addition of the Salt of KY to the solution of MY and NY3 will have no effect on their solubilities.
Consider the following liquid-vapour equilibrium
Which of the following relations is correct?
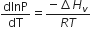

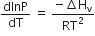
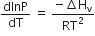
If the value of an equilibrium constant ofr particular reaction is 1.6 x1012 then at equilibrium the system will contains
all reactants
mostly reactants
mostly products
mostly products
The Ksp of Ag2CrO4, AgCl, AgBr and AgI are respectively, 1.1 x 10-12, 1.8 x 10-11, 8.3 x 10-17. Which one of the following salts will precipitate last if AgNO3 solution is added to the solution containing equal moles of NaCl, NaBr, NaI and Na2CrO4?
AgI
AgCl
AgBr
AgBr
For the reversible reaction,
the equilibrium shifts in the forward direction
by increasing the concentration of NH3 (g)
by decreasing the pressure
by decreasing the concentrations of N2 (g) and H2(g)
by decreasing the concentrations of N2 (g) and H2(g)
