 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe reaction![]() is at equilibrium,
is at equilibrium, ![]() formed is absorbed in sulphuric acid, what happens to the equilibrium?
formed is absorbed in sulphuric acid, what happens to the equilibrium?
In a gaseous system at equilibrium ![]() 3 mole of inert gas is pumped into the vessel at constant pressure. What will be its effect on equilibrium?
3 mole of inert gas is pumped into the vessel at constant pressure. What will be its effect on equilibrium?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type
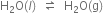

 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat is the effect of pressure on the solubility of a gas in a liquid?
Or
State Henry's Law.
A liquid is in equilibrium with its vapour in a sealed container at a fixed temperature. The volume of the container is suddenly increased.
(i) What is the initial effect of the change on vapour pressure?
(ii) How do rates of evaporation and condensation change initially?
(iii) What happens when equilibrium is restored finally and what will be the final vapour pressure?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type