 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe ionisation constant of acetic acid is 1.74 x10-5. calculate the degree of dissociation of acetic acid in its 0.05M solution. calculate the concentration of acetate ion in the solution and its pH.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeOne mole of ![]() and one mole of CO are taken in a 10-litre vessel and heated to 725K. At equilibrium, 40% of water (by mass) reacts with carbon monoxide according to the equation
and one mole of CO are taken in a 10-litre vessel and heated to 725K. At equilibrium, 40% of water (by mass) reacts with carbon monoxide according to the equation![]()
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type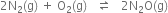
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeNitric oxide reacts with Br2 and gives nitrosyl bromide as per reaction given below:
![]()
When 0.087 mol of NO and 0.0437 mol of Br2 are mixed in a closed container at constant temperature, 0.0518 mol of NOBr is obtained at equilibrium. Calculate equilibrium amount of NO and Br2.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeAt 700K, equilibrium constant for the reaction:

![]()
is 54.8. If 0.5 mole/litre of HI(g) is present at equilibrium at 700K, what are the concentration of H2(g) and I2(g) assuming that we initially started with HI(g) and allowed it to reach equilibrium at 700 K?
Ethyl acetate, is formed by the reaction of ethanol and acetic acid and equilibrium is represented as![]()
(i) Write the concentration ratio (reaction quotient), Qc, for this reaction (note:water is not in excess and is not a solvent in this reaction).
(ii) At 293K, if one starts with 1·00 mol of acetic acid and 0·18 mol of ethanol, there is 0·171 mol of ethyl acetate in the final equilibrium mixture. Calculate the equilibrium constant.
(iii) Starting with 0·5 mole of ethanol and 1·0 mole of acetic acid and maintaining it at 293K, 0·214 mole of ethyl acetate is formed after sometime. Has equilibrium been reached ?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(i) Why some concentrated sulphuric acid is usually added to the reaction mixture in a laboratory preparation of ethyl acetate?
(ii) Since the heat of reaction is nearly zero for this reaction, how will the equilibrium constant depend on upon the temperature?
(i) Concentrated sulphuric acid is a dehydrating agent. It can absorb water. According to Le-Chatelier’s principle, the removal of water from the reaction mixture, equilibrium will shift in the forward direction producing more of ethyl acetate.
(ii) Since the heat of reaction is nearly zero, the equilibrium constant is almost not affected by temperature.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type