 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeLet at equilibrium,

The reaction is

Initial pressure 4.0 atm 0 0
At equm. 4 - p p p
Applying the law of chemical equilibrium
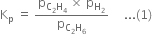
Putting the reaction in expression (1),
we have
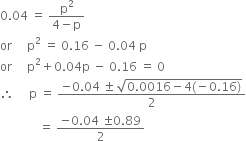
Taking positive value,

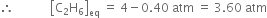
Bromine monochloride (BrCl) decomposes into bromine and chlorine and attains the equilibrium:![]()
for which Kc = 32 at 500 K. If initially pure BrCl is present at a concentration of 3·30×10–3 mol L–1 what is its molar concentration in the mixture at equilibrium?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe value of ![]() for the phoshorylation of glucose in glycolysis is 13.8 kJ/mol. Find the value of Kc at 298 K.
for the phoshorylation of glucose in glycolysis is 13.8 kJ/mol. Find the value of Kc at 298 K.
Hydrolysis of sucrose gives,![]()
Equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction is ![]() Calculate
Calculate ![]() at 300K.
at 300K.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeFind out the value of Kc for each of the following equilibria from the value of Kp:
2NOCl(g) ![]() 2NO(g) + Cl2(g); Kp = 1.8 x 10-2 at 500 K
2NO(g) + Cl2(g); Kp = 1.8 x 10-2 at 500 K
