 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type
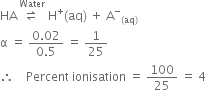
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite the correct balanced net ionic equation for the reaction whose equilibrium constant at 298K is:
(i) Ka(C6H5COOH) = 6·3 × 10–5
(ii) Ka(H2C2O4) = 5·4 × 10–2
(iii) Ka ( HSO3–) = 2·8 × 10–7
(iv) Kb(OCl–) = 9·1 × 10–7
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type