 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeCalculate the degree of hydrolysis of 0.015 M solution of NH4Cl. Given Kb for NH4OH is 1·8 × 10–5, Kw = 10–14at 25°C.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeShow with an example how buffer solution resists the action of acid or base towards change in pH.
Or
Discuss the buffer action of:
(i) acidic buffer
(ii) basic buffer.
Calculate the pH of:
(i) an acidic buffer mixture
(ii) a basic buffer mixture.
Or
Derive Henderson’s equation for an acidic and basic buffer mixture.
Or
Derive the following equation for the pH of an acidic buffer:![]()


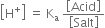
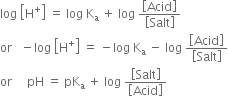
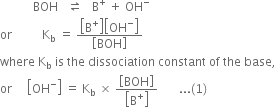
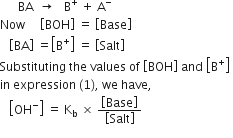
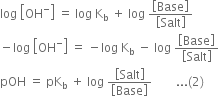
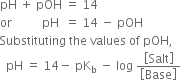
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDescribe Ostwald’s theory of acid-base indicators.
Or
How does Ostwald’s theory explain the colour change of:
(i) Phenolphthalein
(ii) Methyl orange in acid-base titrations?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow does the concept of solubility product help in finding out the solubility of sparingly soluble salts?
