 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is the function of NH4Cl in group V analysis?
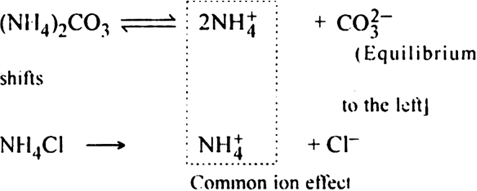
Due to common ion effect of NH4+ ions, the degree of dissociation of (NH4)2CO3 is suppressed, so the concentration of  ions decreases. Thus. ionic product of carbonates of group V cations decreases. Even the low concentration of
ions decreases. Thus. ionic product of carbonates of group V cations decreases. Even the low concentration of  ions is sufficient for the ionic product of these ions and cations of the fifth group to exceed the solubility product of corresponding carbonates. Hence, the carbonates of the fifth group get precipitated.
ions is sufficient for the ionic product of these ions and cations of the fifth group to exceed the solubility product of corresponding carbonates. Hence, the carbonates of the fifth group get precipitated.
Other group cations (Na+, K+ and NH4+ ) are either soluble or their solubility product (in the case of Mg2+) is higher.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeGive reason: The precipitation of Mg(OH)2 is prevented by the addition of NH4Cl prior to the addition of NH4OH. But its precipitation by NaOH is not prevented by the prior addition of NaCl.
In which of the following, silver chloride will dissolve more:
(i) Pure water
(ii) 0·1M AgNO3 solution?
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe equilibrium constant at 298 K for a reaction A+B ⇌ C+D is 100. If the initial concentration of all the four species were 1 M each, then equilibrium concentration of D (in mol L−1 ) will be:
0.818
1.818
1.182
1.182
For the reaction,
if Kp = Kc (RT)x where the symbol has usual meaning then the value of x is (assuming ideality)
-1
-1/2
1/2
1/2
The species which can best serve as an initiator for the cationic polymerization is
LiAlH4
HNO3
AlCl3
AlCl3
The equilibrium constant (Kc) for the reaction, N2(g) + O2 (g) → 2NO (g) at temperature T is 4 x 10-4. The value of Kc for the reaction  at the same temperature is
at the same temperature is
0.02
2.5 x 102
4 x 10-4
4 x 10-4
