 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWrite down the reactions taking place in different Zones in the blast furnance during the extraction of Iron.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow can you separate alumina from silica in a baxuite ore associated with silica? Give equations, if any.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeName the processes from which chlorine is obtained as a bye-product. What will happen if an aqueous solution of NaCl is subjected to electrolysis?
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods:
(i) Zone refining.
(ii) Electrolytic refining.
(iii) Vapour phase refining.
(i) Zone refining: The method is based on the principle that the impurities are more soluble in the melt than the pure metal. A circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of the impure metal. The heater is slowly moved forward. The melted zone moves along with the heater. As the heater moves forward the pure metal crystallizes out of the melt while the impuri-ties pass into the adjacent molten zone. The process is repeated a number of times until the desired state of purity is reached. The end of the rod where the impurities finally get concentrated is cut off.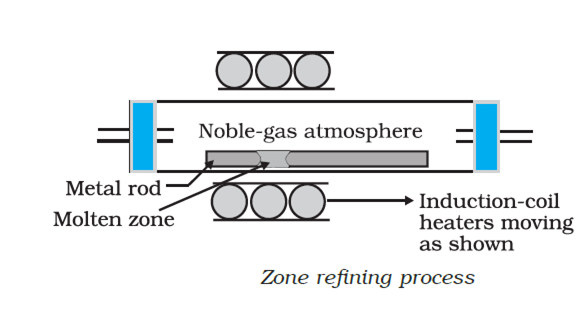
(ii) Electrolytic refining: The impure metal is made the anode and a pure strip of the same metal the cathode in a suitable electrolytic both.
Anode : M → Mn+ + ne–
Cathode: Mn+ + ne– → M
The net result is the transfer of pure metal from the anode to the cathode. The applied voltage is such that more electropositive metals (impurity) remain as ions in the bath whereas the less electropositive metals (impurities) remain unionized and fall done as anode mud.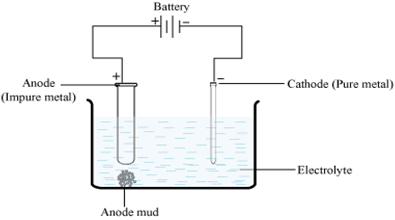
(iii) Vapour phase refining:
(a) Mond Process: Nickel when heated in a stream of carbon monoxide forms volatile nickel carbonyl, Ni(CO)4. The carbonyl vapour when subjected to still higher temperature undergoes thermal decomposition giving pure metal.
(b) Van Arkel Process: Zirconium (or titanium) is heated in iodine vapour at about 870 K to form volatile Znl4. The latter when heated over a tungsten filament at 2075 K decomposes to give pure zirconium.
