 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypePredict the order of reactivity of the following compounds in SN1 and SN2 reactions:
(a) The four isomeric bromobutanes.
(b) C6H5 H2Br, C6H5CH (C6H5Br, C6H5CH (CH3)Br, C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy (-NO2) group shows its effect only at ortho- and para-position and not at meta–position?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type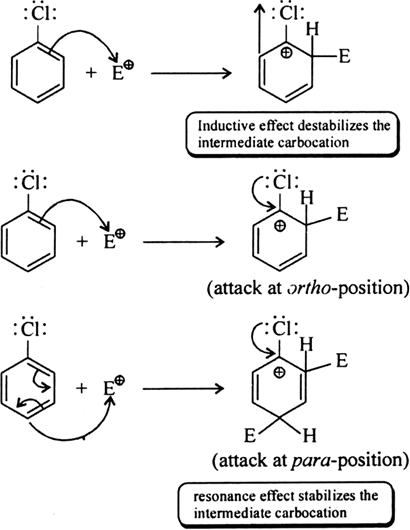
Through resonance, halogen tends to stabilise the carbocation and the effect is more pronounced at ortho- and para- positions. The
inductive effect is stronger than resonance and causes net electron withdrawal and thus causes net deactivation. The resonance effect tends to oppose the inductive effect for the attack at ortho- and parapositions and hence makes the deactivation less for ortho- and paraattack.
Reactivity is thus controlled by the stronger inductive effect and orientation is controlled by resonance effect.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain the reason:
The reactivity order of alkyl bromides is tert alkyl bromide > sec alkyl bromide > primary alkyl bromide.
