 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeSodium salt of which acid will be needed for the preparation of propane? Write chemical equation for the reaction.
What happens when:
(i) Propyne is heated with H2 in the presence of nickel at 473 K?
(ii) Water is dropped on aluminium carbide?
(iii) Sodium propionate is heated with sodalime?
(iv) Acetic acid is treated with hydroiodic acid in the presence of red phosphorus at 420 K?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeAssign reasons for the following:
(i) Boiling points of n-alkanes increase regularly with the increase in the number of carbon atoms.
(ii) Branched-chain alkanes have lesser boiling points than the straight chain alkanes.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAssign reasons for the following:
(i) All C-H bonds in methane are equivalent.
(ii) Alkanes are called paraffins.
Alkanes with even carbon atoms have higher melting points than alkanes with an odd number of carbon atoms.Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDescribe substitution reaction with special reference to halogenation of alkane.
Substitution reaction: A substitution reaction is that which involves the direct replacement of hydrogen atoms of some other groups of a molecule by suitable atoms or groups without changing the structure of remaining part of the molecule. The product obtained is known as substitution product and new atom or group which enters the molecule is known as a substituent.
Halogenation: It involves the replacement of one or more hydrogen atom(s) of alkane by the corresponding number of a halogen atom(s).
(i) Chlorination: Chlorination of alkanes is carried out by treating alkane with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light or at 523-673 K temperature.
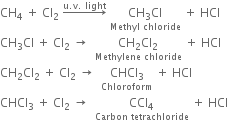
(ii) Bromination: Bromination takes place similarly but not so rapidly.
(iii) Iodination: Iodination is extremely slow and reversible due to the reducing nature of HI.
Thus, iodination is carried out in the presence of some oxidising agent like iodic acid (HIO3) of nitric acid (HNO3) which converts HI to iodine and pushes the reaction in the forward direction.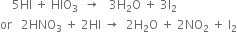
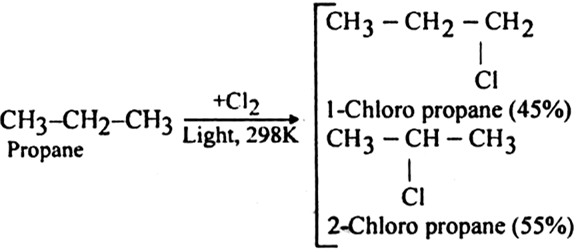
Halogenation of higher alkanes (ethane, propane etc), yields a mixture of all possible isomerism products. 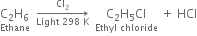
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy does the iodination of methane require an oxidising agent while so much reagent is needed in the chlorination and bromination of methane?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type