 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeSodium salt of which acid will be needed for the preparation of propane? Write chemical equation for the reaction.
What happens when:
(i) Propyne is heated with H2 in the presence of nickel at 473 K?
(ii) Water is dropped on aluminium carbide?
(iii) Sodium propionate is heated with sodalime?
(iv) Acetic acid is treated with hydroiodic acid in the presence of red phosphorus at 420 K?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeAssign reasons for the following:
(i) Boiling points of n-alkanes increase regularly with the increase in the number of carbon atoms.
(ii) Branched-chain alkanes have lesser boiling points than the straight chain alkanes.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAssign reasons for the following:
(i) All C-H bonds in methane are equivalent.
(ii) Alkanes are called paraffins.
Alkanes with even carbon atoms have higher melting points than alkanes with an odd number of carbon atoms.Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy does the iodination of methane require an oxidising agent while so much reagent is needed in the chlorination and bromination of methane?
Iodine reacts with methane molecules reversibly. In fact, hydrogen iodide formed is a very strong reducing agent and it can convert iodomethane back to methane.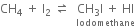
To overcome this difficulty, iodination is generally carried out in the presence of strong oxidising agents like iodic acid (HIO3) which oxides HI formed during the reaction to iodine. 
On the other hand, during the chlorination or bromination of methane, no such reducing agent is produced.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type