 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeGive IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(a) CH3CH = (CH3)2
(b) CH2 = CH – C ≡ C – CH3
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWrite structure and IUPAC names of different structural isomers of alkenes corresponding to C5H10.
What is meant by hindered (or restricted) rotation around carbon-carbon double bond? What type of isomerism does it lead to?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat are the necessary and sufficient conditions for a compound to exhibit geometrical isomerism ?
Conditions for geometrical isomerism: There are two necessary conditions for a compound to possess geometrical isomerism:
(i) It must contain a carbon-carbon double bond in the molecule.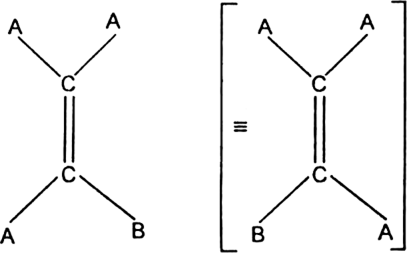
(ii) Two unlike atoms or groups must be linked to each doubly bonded carbon atoms.
Geometrical isomerism among alkenes does not occur when the doubly bonded carbon carry identical atoms or groups. For example, AAC = CAB does not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
Name the various structural isomers possible in C4H8. Which one will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
