 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat happens when:
(i) Ethyl alcohol is heated in the presence of Al2O3 at 493 K?
(ii) Ethylene dibromide is heated with zinc dust?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy are alkenes more reactive than alkanes ?
Alkenes have a carbon-carbon double bond (>C = C<) in their molecules. The >C = C< bond is made up of one strong σ bond and one weak  bond. The electrons of the
bond. The electrons of the 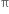 bond are more exposed which increase reactivity. In other words, the presence of
bond are more exposed which increase reactivity. In other words, the presence of 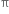 bond (formed by the sideways overlapping of atomic orbital) makes alkenes highly reactive chemically as compared to alkanes.
bond (formed by the sideways overlapping of atomic orbital) makes alkenes highly reactive chemically as compared to alkanes.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDiscuss the mechanism of addition hydrogen acids to symmetrical alkenes. Justify the order of reactivity of halogen acids HI > HBr > HCl.
