Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat happens when:
(i) Ethyl alcohol is heated in the presence of Al2O3 at 493 K?
(ii) Ethylene dibromide is heated with zinc dust?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDiscuss the mechanism of addition hydrogen acids to symmetrical alkenes. Justify the order of reactivity of halogen acids HI > HBr > HCl.
Alkenes react with halogen acids to form mono-haloalkanes called alkyl halides.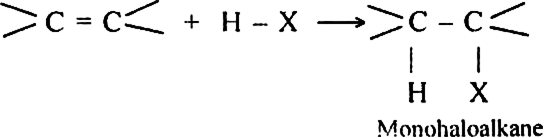
The order of reactivity of the halogen acids is HI > HBr > HCl.
The above order is justified on the basis of bond dissociation energies of the halogen acids.
HI (300 kJ mo-1) < HBr (365 kJ mol-1) < HCl (430 kJ mor-1) For example,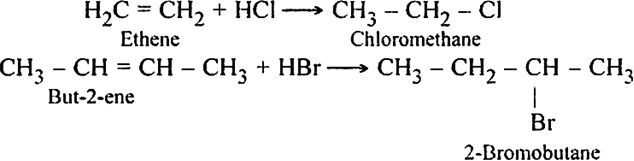
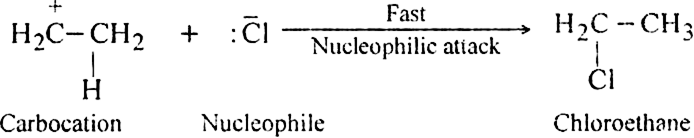
Mechanism: It is electrophilic addition reaction and consists of the following steps:
(i) Electromeric effect and electrophilic attack:
(ii) Attack of nucleophile: The nucleophile released in the slow step combines with carbocation to give chloroethane.