 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDiscuss the free radical mechanism of addition of HBr to propene.
Or
Give the mechanism of addition of HBr to propylene in the presence of peroxide.
The addition of HBr to propene yields 2-broniopropane, while in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields 1-bromopropane. Explain and give mechanism.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy peroxide effect is shown only by HBr and not by HCl or HI?
Or
Explain why Kharasch effect is shown by HBr only and not by HCl or HI.
The mechanism of addition of HBr to a unsymmetrical alkene (say propene) in the presence of peroxide is free radical i.e. "H-Br undergoes homolysis to form free radical.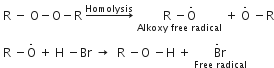
HCl is a very stable acid H-Cl bond (430 kJ moH) is stronger than H-Br bond (378 kJ mol-1) and is not broken symmetrically by the free radicals generated by peroxide. Hence the free radical addition of HCl to alkenes is not possible.
In the case of HI, the H - I bond (297 kJ mo-1) is weaker than H-Br bond and undergoes homolysis readily to form iodine free radical. But iodine free radicals have greater tendency to combine amongst themselves to form iodine molecules rather than add to the ethylenic bond.
Hence HI does not respond to the peroxide effect.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite IUPAC names of the products obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compounds:
Pent - 2-ene
Write IUPAC names of the products obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compounds:
3, 4-Dimethlhept-3-ene
