 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDiscuss the acidic character of alkynes.
Alkynes with a triple bond in the terminal position (– C ≡ C – H) are very weakly acidic in nature. They do not turn blue litmus red but give hydrogen with metals like sodium.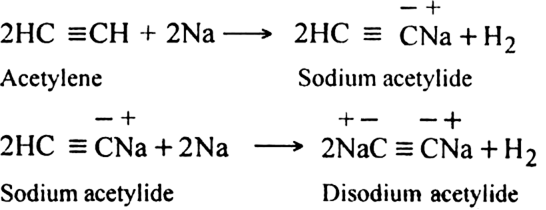
Explanation: The hydrogen atom attached to the triply bonded carbon atom ( C – C ≡ C – H) is called acetylenic hydrogen. The acidic character of alkyne having acetylenic hydrogen (HC ≡C –H, CH3 – C ≡ C – H, etc.) is explained by hybridization phenomenon. The carbon atom in ≡ C–H bond beings hybridised (50%, s-character) is quite electronegative in nature. It can readily accept the electron pair from the C-H bond. Consequently, the H+ ion can be easily released and this accounts for the weakly acidic character of alkynes.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeArrange benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in decreasing order of acidic behaviour. Also give reason for his behaviour.
Give simple chemical test for the distinction of:
(i) Propyne and propane
(ii) But-1-yne and But-2-yne.
