 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat happens when:
Benzene is treated with n-propyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeHow benzene is converted into benzene sulphonic acid? Give its mechanism.
Or
Explain the mechanism of sulphonation of benzene.
Discuss the mechanism of Friedel Craft’s reaction.
Or
Discuss the mechanism of Friedel Craft’s alkylation of benzene. Give the mechanism of reaction of benzene within ![]() the presence of AlCl3.
the presence of AlCl3.
Or
How is benzene converted into aceto-phenone? Name the reaction and discuss the mechanism explaining each step.
Or
Give the mechanism of acylation of benzene.
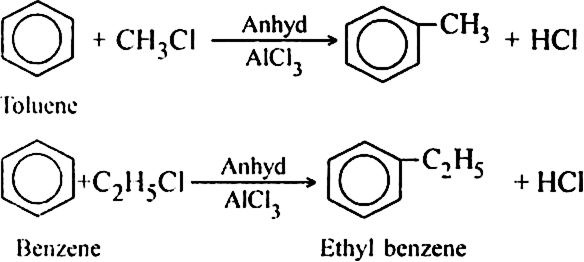
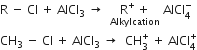
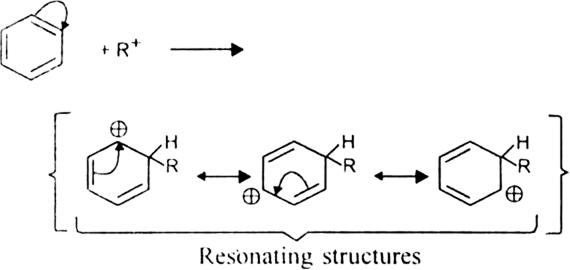

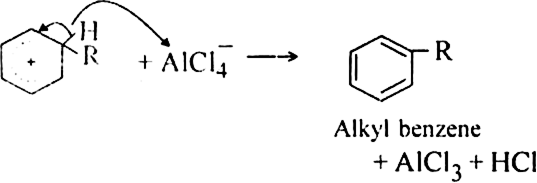
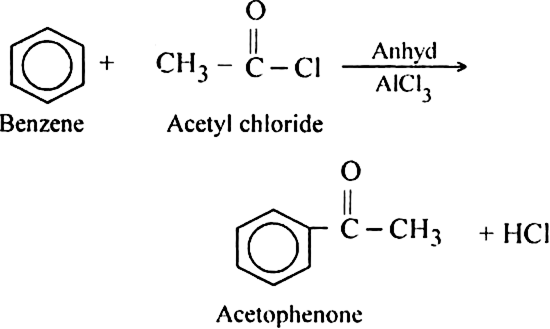
Mechanism: It involves following steps:
(i) Generation of electrophile.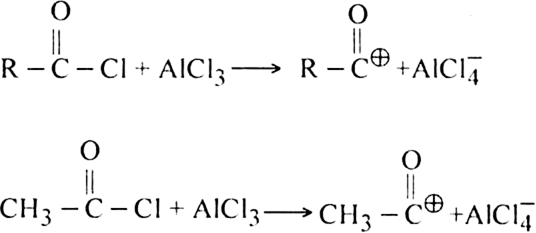
(ii) Formation of the carbocation.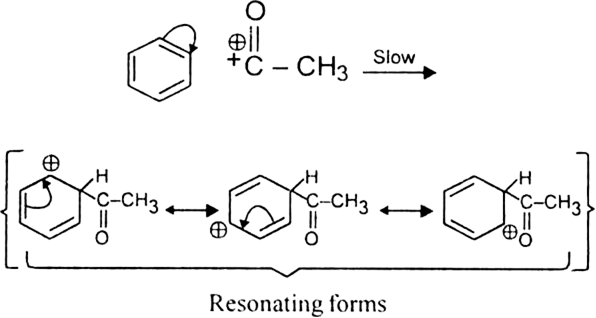
The resonance hybrid structure of the above resonating forms can be represented as: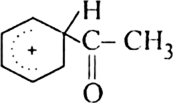
(iii) Proton transfer from the carbocation to form the final product. 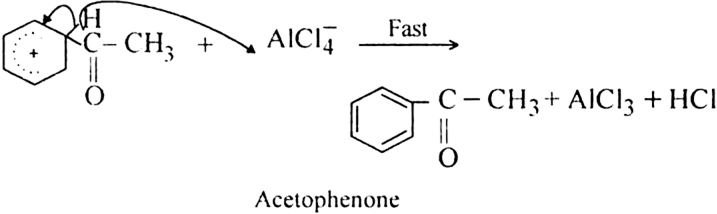
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy does benzene undergo electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type