 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo organic compounds X and Y on analysis gave the same percentage composition namely; C = (12/13) × 100% and H = (1/13) × 100%. However, compound X decolourises bromine water while compound Y does not. The two compounds X and Y may be respectively
acetylene and ethylene
acetylene and benzene
ethylene and benzene
toluene and benzene
For preparing an alkane, a saturated solution of sodium or potassium salt of a carboxylic acid is subjected to
hydrolysis
electrolysis
oxidation
hydrogenation
The reaction of ![]() with HBr gives predominantly
with HBr gives predominantly
![]()



A.
![]()
The addition of HBr to an alkene is an example of electrophilic addition reactions. It takes place by following mechanism.

An organic compound with molecular formula C6H12 upon ozonolysis give only acetone as the product. The compound is
2,3-dimethyl-1-butene
3-hexane
2-hexene
2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
An aromatic hydrocarbon with empirical formula C5H4 on treatment with concentrated H2SO4 gave a monosulphonic acid. 0.104 g of the acid required 10 mL of NaOH for complete neutralisation. The molecular formula of hydrocarbon is
C5H4
C10H8
C15H12
C20H16
An alkene having the molecular formula C9H18 on ozonolysis gives 2, 2-dimethyl propanal and 2-butanone. The alkene is :
2, 2, 2-trimethyl-3-hexene
2, 2, 6-trimethyl-3-hexane
2, 3, 4-trimethyl-2-hexene
2, 2, 4-trimethyl-3-hexene
Observe the following reactions and predict the nature of A and B:
A and B both are 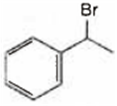
A and B both are ![]()
A is 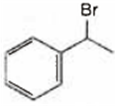 and B is
and B is ![]()
A is ![]() and B is
and B is 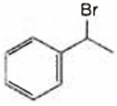
Nitration of aniline in strongly acidic medium, result in the formation of m-nitroaniline also. This is because :
amino group is meta orienting during electrophilic substitution reaction
nitro group goes always to the meta position irrespective of the substituents
nitration of aniline is a nucleophilic substitution reaction in strongly acidic medium
in strongly acidic conditions aniline is present as anilinium ion
