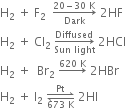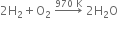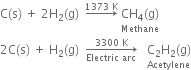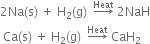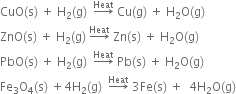Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is water gas? How will you prepare hydrogen from water gas?
Or
How is dihydrogen prepared on a commercial scale?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow will you prepare hydrogen commercially from hydrocarbons?
Or
What is understood by ‘water gas shift reaction’? Discuss its use for the preparation of hydrogen.
Describe the bulk preparation of hydrogen by an electrolytic method. What is the role of electrolyte in this process?
Or
How is dihydrogen manufactured by the electrolysis of water?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeHow does dihydrogen react with:
(a) non-metals (b) metals and (c) metal oxides?