 Long Answer Type
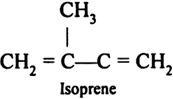
Long Answer TypeElaborate the structure of natural rubber.

Give the monomers and uses of each of the following addition polymers:
(a) Polyethylene
(b) Polypropylene
(c) Polystyrene.
What are linear polymer and branched chain polymers? How do these differ from own linked polymers?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDefine a polymer. Write the monomer used for the preparation of dacron. Mention a use of it.
Write the names and molecular structure of the monomers of the following:
(i) Natural rubber (ii) Neoprene.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Polystyrene (ii) Neoprene.
