 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Glyptal
(iii) Polyvinyl chloride
Define thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give one example of each.
Thermoplastic Polymers: These are the linear or slightly branched long chain molecules capable of repeatedly softening on heating and hardening on cooling. These possess intermolecular forces of attraction intermediate between elastomers and fibres. For e.g. Polythene, Polyvinyl etc.
Thermosetting Polymers: These are cross-linked or heavily branched molecules which on heating undergo extensive cross-linking in moulds and again become invisible. These cannot be reused. For e.g. bakelite, urea-formaldehyde resins etc.
What is a biodegradable polymer? Give an example of biodegradable aliphatic polyester.
Differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give one example of each.
(i) What is the role of t-butyl peroxide in the polymerization of ethene?
(ii) Identify the monomers in the following polymer:
OR
Write the mechanism of free radical polymerization of ethene.
i) What is the role of sulphur in the vulcanization of rubber?
ii) Identify the monomers in the following polymer: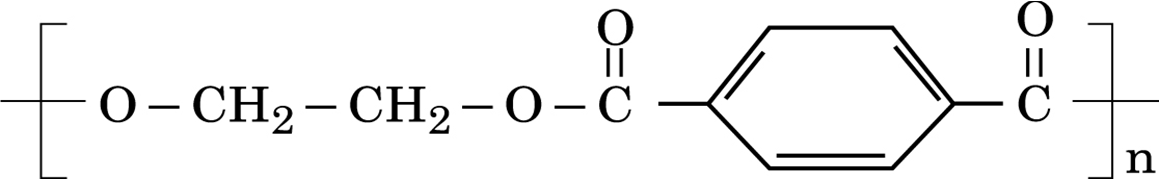
iii)Arrange the following polymers in the increasing order of their intermolecular forces:
Terylene, polythene, Neoprene
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Dacron
(iii) Neoprene