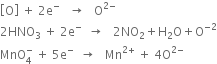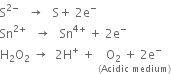Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe standard electrode potentials of elements A, B and C are + 0.68, -2 .50 and -0.50 V respectively. Write the correct order of their reducing power.
In the standardisation of Na2S2O3 using K2Cr2O7 by iodometry, calculate the equivalent mass of K2Cr2O7?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDefine oxidising agents and reducing agents in terms of electronic concept ?