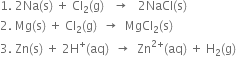Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeShow that oxidation cannot occur without reduction.
Or
Show that oxidation and reduction go side by side.
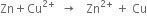
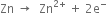


 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type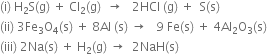
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat are the changes which take place when a redox reaction is carried in a beaker? Explain with the help of a suitable example.
Or
Explain the redox reaction
occurring in a beaker.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type