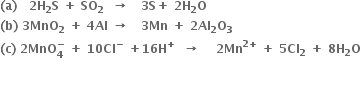Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeConsider the elements:
Cs, Ne, I and F.
(a) Identify the element that exhibits only negative oxidation state.
(b) Identify the element that exhibits only positive oxidation state.
(c) Identify the element that exhibits both positive and negative oxidation states.
(d) Identify the element which exhibits neither negative nor positive oxidation state.
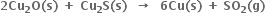
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(b) HCHO(l) + 2[Ag (NH3)2]+ (aq) + 3OH-(aq) → 2Ag(s) + HCOO–(aq) + 4NH3(aq) + 2H2O(l)
(c) HCHO (l) + 2 Cu2+ (aq) + 5 OH–(aq) → Cu2O(s) + HCOO-(aq) + 3H2O(l)
(d) N2H4(l) + 2H2O2(l) → N2(g) + 4H2O(l)
(e) Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
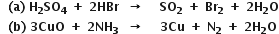
a) AgBr is reduced to Ag
C6H6O2 is oxidised to C6H4O2
AgBr is an oxidising agent
C6H6O2 is a reducing agent.
b) [Ag(NH3)+2 reduced to Ag+
HCHO is oxidised to HCOO-
[Ag(NH3)+2 is an oxidising agent.
c) HCHO is oxidised to HCOO-
Cu2+ is reduced to Cu(I) state.
d) N2H4 is reduced to H2O
H2O2 is an oxidising agent
N2H4 is reducing agent.
e) Pb has been oxidised to PbSO4
PbO2 is reduced to PbSO4
PbO2 is an oxidising agent
Pb is a reducing agent.