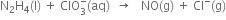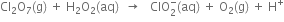Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type

1. Write the oxidation and reduction half-reactions by observing the changes in oxidation numbers and write these separately.
Oxidation half-reaction: 
Reduction half-reaction: 
2. Balancing the oxidation half reaction.
(i) The balance I atoms are done by multiplying HIO3 by 2.
0 +5

(ii) Add 10 electrons towards R.H.S. in order to balance the changes on iodine atoms.

(iii) Balance the O atoms by adding six H2O molecules towards L.H.S.

(iv) Balance H atoms by adding ten H+ towards
R.H.S.

3. Balancing the reduction half reaction.
(i) Balancing of N is not required as the number of each N is one on both the sides.
+5 +4
HNO3  NO2
NO2
(ii) Add one electron towards L.H.S. in order to balance the charges on the nitrogen atom.
+5 +4
HNO3 + e-  NO2
NO2
(iii) Balance O atoms by adding one H2O molecule towards R.H.S.
5 4
HNO3 + e-  NO2 + H2O
NO2 + H2O
(iv) Balance H atoms by adding one H+ towards
L.H.S.
+5 +4
HNO3 + H+ + e-  NO2 + H2O
NO2 + H2O
(Balance reduction half reaction)
4. Multiply balanced reduction half-reaction by 10 to equate electrons and add both the half reactions.

This is a balanced redox reaction.
Chlorine is used to purify drinking water. Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess of chlorine is removed by treating with sulphur dioxide. Present a balanced equation for this redox change taking place in water.
The Mn3+ ions is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2 and H+ ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypePermanganate (VII) ion,  in basic solution oxidises iodide ion, I- to produce molecule iodine (I2) and manganese (IV) oxide (MnO2). Write a balanced ionic equation to represent redox reaction.
in basic solution oxidises iodide ion, I- to produce molecule iodine (I2) and manganese (IV) oxide (MnO2). Write a balanced ionic equation to represent redox reaction.
Balance the following equations in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number method: