 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsOn mixing, heptane and octane form an ideal solution. At 373 K, the vapour pressures of the two liquid components (heptane and octane) are 105 kPa and 45 kPa respectively.Vapour pressure of the solution obtained by mixing 25.0 g of heptane and 35 g of octane will be (molar mass of heptane = 100 g mol–1 and of octane =114 g mol–1)
144.5 kPa
72.0 kPa
36.1 kPa
36.1 kPa
The freezing point of benzene decreases by 0.45°C when 0.2 g of acetic acid is added to 20 g of benzene. If acetic acid associates to form a dimer in benzene, percentage association of acetic acid in benzene will be
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol–1)
64.6%
80.4%
74.6%
74.6%
On treatment of 100 mL of 0.1 M solution of CoCl3 . 6H2O with excess AgNO3; 1.2 × 1022 ions are precipitated. The complex is
[Co(H2O)4 Cl2]Cl.2H2O
[Co(H2O)3Cl3].3H2O
[Co(H2O)6]Cl3
[Co(H2O)6]Cl3
1 gram of a carbonate (M2CO3) on treatment with excess HCl produces 0.01186 mole of CO2. The molar mass of M2CO3 in g mol-1 is
1186
84.3
118.6
118.6
Two liquids X and Y form an ideal solution. At 300 K, the vapour pressure of the solution containing 1 mol of X and 3 mol of Y is 550mm Hg. At the same temperature, if 1 mol of Y is further added to this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10 mm Hg. Vapour pressure (in mmHg) of X and Y in their pure states will be respectively
200 and 300
300 and 400
400 and 600
400 and 600
A binary liquid solution is prepared by mixing n-heptane and ethanol. Which one of the following statements is correct regarding the behaviour of the solution?
The solution formed is an ideal solution
The solution is non-ideal, showing +ve deviation from Raoult’s law.
The solution is non-ideal, showing –ve deviation from Raoult’s law.
The solution is non-ideal, showing –ve deviation from Raoult’s law.
At 80o C, the vapour pressure of pure liquid ‘A’ is 520 mm Hg and that of pure liquid ‘B’ is 1000 mm Hg. If a mixture solution of ‘A’ and ‘B’ boils at 80o C and 1 atm pressure, the amount of ‘A’ in the mixture is (1 atm = 760 mm Hg)
52 mol percent
34 mol percent
48 mol percent
48 mol percent
The vapour pressure of water at 20oC is 17.5 mm Hg. If 18 g of glucose (C6H12O6) is added to 178.2 g of water at 20oC, the vapour pressure of the resulting solution will be
17.675 mm Hg
15.750 mm Hg
16.500 mm Hg
16.500 mm Hg
Equal masses of methane and oxygen are mixed in an empty container at 25ºC. The fraction of the total pressure exerted by oxygen is
2/3
(1/3) x (273 / 298)
1/3
1/3
C.
1/3
Let the mass of methane and oxygen is w
mole fraction of oxygen 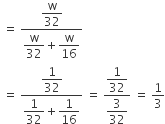
Let the total pressure be P The pressure exerted by oxygen (partial pressure) = XO2 × Ptotal
P =1/3
A 5.25% solution of a substance is isotonic with a 1.5% solution of urea (molar mass = 60 g mol–1) in the same solvent. If the densities of both the solutions are assumed to be equal to 1.0 gcm–3, molar mass of the substance will be –
90.0g mol–1
115.0g mol–1
105.0g mol–1
105.0g mol–1
