 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe density (in g mL–1) of a 3.60 M sulphuric acid solution that is 29% H2SO4 (Molar mass = 98 g mol-) by mass will be
1.64
1.88
1.22
1.22
A mixture of ethyl alcohol and propyl alcohol has a vapour pressure of 290 mm at 300 K. The vapour pressure of propyl alcohol is 200 mm. If the mole fraction of ethyl alcohol is 0.6, its vapour pressure (in mm) at the same temperature will be
350
300
360
360
A.
350
Let the vapour pressure of pure ethyl alcohol be P,
According to Raoult’s law 290 = 200 × 0.4 + P × 0.6
P = 290-80/0.6 = 350 mm Hg
Density of a 2.05 M solution of acetic acid in water is 1.02 g/mL. The molality of the solution is
1.14 mol kg–1
3.28 mol kg–1
2.28 mol kg–1
2.28 mol kg–1
18 g of glucose (C6H12O6) is added to 178.2 g of water. The vapour pressure of water for this aqueous solution at 100o C is
759.00 Torr
7.60 Torr
76.00 Torr
76.00 Torr
The volume of a colloidal particle, VC as compared to the volume of a solute particle in a true solution VS, could be
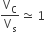
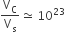
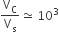
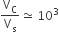
The solubility product of a salt having general formula MX2, in water is 4 x 10-12. The concentration of M2+ ions in the aqueous solution of the salt is
2.0 x 10-6 M
1.0 x 10-4 M
1.6 x 10-4 M
1.6 x 10-4 M
Benzene and toluene form nearly ideal solutions. At 20o C, the vapour pressure of benzene is 75 torr and that of toluene is 22 torr. The partial vapour pressure of benzene at 20o C for a solution containing 78 g of benzene and 46 g of toluene in torr is
50
25
37.5
37.5
Two solutions of a substance (non-electrolyte) are mixed in the following manner. 480 ml of 1.5 M first solution + 520 mL of 1.2 M second solution. What is the molarity of the final mixture?
1.20 M
1.50 M
1.344 M
1.344 M
Equimolar solutions in the same solvent have
Same boiling point but different freezing point
Same freezing point but different boiling point
Same boiling and same freezing points
Same boiling and same freezing points
Which one of the following aqueous solutions will exhibit highest boiling point?
0.01 M Na2SO4
0.015 M glucose
0.015 M urea
0.015 M urea
