 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions6.02×1020 molecules of urea are present in 100 ml of its solution. The concentration of urea solution is
0.001 M
0.1 M
0.02 M
0.02 M
To neutralize completely 20 mL of 0.1 M aqueous solution of phosphorous acid (H3PO3), the volume of 0.1 M aqueous KOH solution required is
10 mL
60 mL
40 mL
40 mL
Which of the following liquid pairs shows a positive deviation from Raoult’s law?
Water – hydrochloric acid
Acetone – chloroform
Water – nitric acid
Water – nitric acid
Which one of the following statements is false?
Raoult’s law states that the vapour pressure of a components over a solution is proportional to its mole fraction
Two sucrose solutions of same molality prepared in different solvents will have the same freezing point depression
The correct order of osmotic pressure for 0.01 M aqueous solution of each compound is BaCl2 > KCl > CH3COOH > sucrose
The correct order of osmotic pressure for 0.01 M aqueous solution of each compound is BaCl2 > KCl > CH3COOH > sucrose
The molar solubility product is Ksp. ‘s’ is given in terms of Ksp by the relation
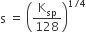

s = (256 Ksp)1/5
s = (256 Ksp)1/5
For 1 molal aqueous solution of the following compounds, which one will show the highest freezing point?
[Co(H2O)3 Cl3].3H2O
[Co(H2O)6]Cl3
[Co(H2O)5Cl] Cl2.H2O
[Co(H2O)4Cl2]Cl.2H2O
A.
[Co(H2O)3 Cl3].3H2O
The complex giving least number of ions will have lowest depression in freezing point and therefore highest freezing point.(Van’t Hoff factor = 1)
An aqueous solution contains an unknown concentration of Ba2+. When 50 mL of a 1 M solution of Na2SO4 is added, BaSO4 just begins to precipitate. The final volume is 500 mL. The solubility product of BaSO4 is 1 x 10–10. What is the original concentration of Ba2+?
1.0 x 10–10 M
5 x 10–9 M
2x10–9 M
1.1 x 10–9M
Assuming the compounds to be completely dissociated in aqueous solution, identify the pair of the solutions that can be expected to be isotonic at the same temperature.
0.01 M urea and 0.01 M NaCl
0.02 M NaCl and 0.01 M Na2SO4
0.03 M NaCl and 0.02 M MgCl2
0.01 M sucrose and 0.02 M glucose
If and p are the vapour pressure of the pure solvent and solution and n1 and n2 are the moles of solute and solvent respectively in the solution then the correct relation between p and p° is
