 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDensity of a gas is found to be 5.46 g/dm3 at 7°C at 2 bar pressure. What will be its density at STP?Â
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIf the density of a gas at the sea level at 0° is 1·29 kg m–3, what is the molar mass? (Assume that pressure is equal to 1 bar).
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type34.05 mL of phosphorus vapours weighs 0.0625 g at 546°C and 0·1 bar pressure. what is the molar mass of phosphorus?
Here P = 0.1 bar;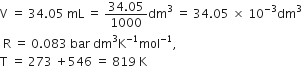
Applying general gas equation,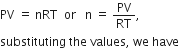
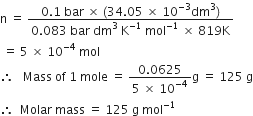
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type2.9 g of a gas at 95°C occupied the same volume as 0·184g of hydrogen at 17°C at the same pressure. What is the molar mass of the gas?Â
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeCalculate the mass of methane in a 9L cylinder at 16 bar and 27°C. (R = 0·08L bar K–1 mol–1).
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeTwo flasks A and B have equal volumes. Flask A contains H2 and is maintained at 300K while the flask B contains an equal mass of CH4 gas and is maintained at 600K. In which flask is the pressure greater? How many times ?
Pressure of 1g of an ideal gas A at 27° C is found to be 2 bar. When 2g of another ideal gas B is introduced in the same flask at same temperature the pressure becomes 3 bar. Find a relationship between their molecular masses.
Pay load is defined as the difference between the mass of displaced air and the mass of the balloon. Calculate the pay load when a balloon of radius 10 m, mass 100 kg is filled With helium at 1·66 bar at 27°C. (Density of air = 1·2 kg m-3 and R = 0·083 bar dm3 K–1 mo1–1).Â
