 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeUsing s, p, d notations describe the orbital with the following quantum numbers :
(a) n = 1, l = 0,
(b) n = 3, l = 1,
(c) n = 4, l = 2,
(d) n = 4, l = 3.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeState and explain Pauli's Exclusion Principle.
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle: It states: No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of all the four quantum numbers (n, l, m, s).
According to this principle, two electrons in an atom can have a maximum of three quantum numbers identical but the value of the fourth quantum number must be different. Electrons having the same set of values n, l and m are said to belong to the same orbital.
For example, for K shell i.e. when n = 1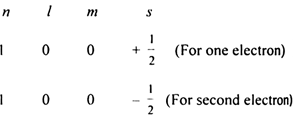
Thus, we conclude from the above that:
(i) an orbital cannot have more than 2 electrons, (ii) if an orbital has two electrons, they must have opposite spin.
Application of Pauli’s Exclusion Principle: The maximum number of electrons in different sub-shells and energy levels can be deduced from this principle.
For L shell (n = 2)
|
n |
l |
m |
s |
|
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 |
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
0 0 -1 -1 0 0 +1 +1 |
+1/2 -1/2 +1/2 +1/2 -1/2 -1/2 +1/2 -1/2 |
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe bromine atom possesses 35 electrons. It contains 6 electrons in 2p orbital, 6 electrons in 3p orbital and 5 electrons in 4p orbital. Which of these electron experiences the lowest effective nuclear charge?
