 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeAnswer:
Enzymes are biological catalysts which increases the rate of cellular reactions.
Mechanism of enzyme catalysis : Enzymes are proteins (globular proteins) and have large molecular masses ranging from 12000 to 40,000. Thus, these are much bigger than the molecules which they catalyse. The substances which are catalysed are known as substrates. The mechanism of the enzyme catalysed reaction is completed in the following steps:
Step-1. Binding enzyme to substrate (reactant) to form a complex.
Step-2. Product formation in the complex:
Step-3. Release of the product from the enzyme complex.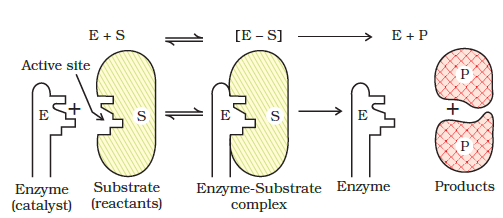
Actually there are a number of cavities present on the surface of the molecules of enzymes. These cavities have specific shapes and contain in their active groups such as – NH2, – COOH, – SH, – OH etc. These function as active sites on the surface of enzyme. The molecules of the reactant (substrate) which have complementary shapes fit into these cavities in the same manner as a key fits into a lock. This results in an activated complex which breaks to give the product and releases the enzyme catalyst.
