 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite two properties of lithium carbonate in which it differs from other alkali metal carbonates.
Why is LiF almost insoluble in water whereas LiCl in soluble not only in water but also in acetone?
How would you explain that the following observations?
LiI is more soluble than KI in ethanol?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain: Lithium exhibits anamalous behaviour in the company of alkali metals.
Or
Name the chief factor responsible for the anomalous behaviour of lithium.
Or
List three properties of lithium in which it differs from the rest of the alkali metals.
Anomalous behaviour of lithium is due to its:
(i) very small size,
(ii) high electronegativity and ionisation energy enthalpy value and
(iii) the absence of d-orbitals in the valence shell of its atom.
Therefore, lithium differs from other members of the family in the following respects:
(i) Lithium is harder than other alkali metals.
(ii) Lithium combines with oxygen to form lithium oxide while other alkali metals form peroxides and superoxides.
(iii) Lithium when heated with ammonia forms imide, Li2NH, while other alkali metals form amides, MNH2 as: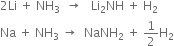
(iv) Lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate decompose on heating while the hydroxides and carbonates of other alkali metals do not decompose on heating.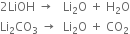
(v) Lithium unlike other alkali metals from no ethynide on reaction with ethyne.
(vi) Lithium nitrate when heated gives lithium oxide, while other alkali metal nitrates decompose to give the corresponding nitrites. 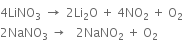
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIn what ways lithium shows similarities to magnesium in its chemical behaviour?
Or
List four properties to show the diagonal relationship between lithium and magnesium.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type