 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat happens when:
(i) sodium carbonate reacts with the milk of lime.
(ii) sodium carbonate is added to water.
(iii) sodium carbonate reacts with a dilute mineral acid?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeHow is sodium hydroxide manufactured? Discuss in brief the details of the process.
Or
With the help of a diagram, show the reactions at the cathode and anode in the manufacture of sodium hydroxide by the Castner - Kellner process.
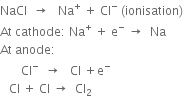

The mercury at the bottom of the cell acts as an intermediate electrode by induction. It serves as the anode in the middle compartment and as a cathode in the outer compartments. These outer compartments are provided with graphite anodes. The saturated brine solution is put in them. The middle compartment contains dilute caustic soda. A series of iron rods fitted in this compartment act as a cathode. On passing electric current, the following reactions occur:
1. In the outer compartments. Sodium chloride solution is electrolyzed. Chlorine is liberated at the anodes. Sodium ions are discharged at the mercury cathode and metallic sodium forms. This combines with mercury forming sodium amalgam (Na-Hg). The sodium amalgam formed is transferred to the central compartment by giving a slight rocking motion to the cell.

At anode:
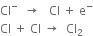
At cathode:
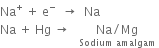
2. In the central compartment. Here sodium-amalgam acts as an anode, while the iron rods act as a cathode. The sodium amalgam reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide. Here, following reactions take place:
At Na-Hg anode.

At iron cathode.
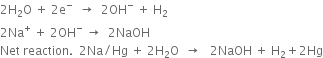
Hydrogen escapes out through an outlet at the top. The strength of sodium hydroxide in the central compartment gradually increases, when it reaches a concentration of about 20%, it is removed and evaporated to get solid sodium hydroxide.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain what happens when:
(i) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated
(ii) Sodium amalgam reacts with water
(iii) Fused sodium metal reacts with ammonia?
Explain the significance of sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium in biological fluids ?
