 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe alkaline earth metals are denser and harder than the corresponding alkali metals. Explain ?
What is the trend of atomic and ionic radii of alkaline earth metals within the group?
The atomic and ionic radii of alkaline earth metals are smaller than those of the corresponding alkali metals. Explain.
How will you explain that alkaline earth metals have much higher melting and boiling points than those of alkali metals?
The first ionisation enthalpies of alkaline earth metals are higher than those of corresponding alkali metals. Explain.
Second ionisation enthalpies of alkali metals are much higher than those of the alkaline earth metals. Explain.
How will you explain the electropositive or metallic character of alkaline earth metals?
Alkaline earth metals are fairly electropositive as their atoms have a tendency to lose their two outermost electrons forming dipositive ions. 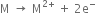
On moving down the group, the atomic radii increase and ionisation enthalpies decrease. Consequently, the electropositive or metallic character increases. Thus, Mg is more electropositive than Be and so on.
