 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeBeryllium and magnesium do not give colour to flame whereas other alkaline earth metals do so. Why?
How will you explain the reducing character of alkaline earth metals?
Except beryllium, the alkaline earth metals have a fairly strong tendency to lose two electrons to form dipositive ions because of their low ionisation enthalpies and high negative value of standard electrode potentials. Therefore, they act as reducing agents.
The reducing character of alkaline earth metals increases as we move down the group from Be to Ba because the ionisation enthalpies increase and electrode potentials become more and more negative with increasing atomic number from Be to Ba.
Comment on each of the following observations: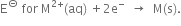
(where M = Ca, Sr or Ba) is nearly constant.
Explain why alkaline earth metals are poor reducing agents as compared to alkali metals.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain the trend of solubility of carbonate, sulphates and hydroxides of alkaline earth metals ?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAccount for the following:
(i) Be(OH)2 is amphoteric while Mg(OH)2 is basic.
(ii) Be(OH)2 is insoluble but Ba(OH)2 is fairly soluble in water.
