 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat do you mean by internal energy and internal energy change?
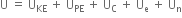
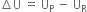


 the extra energy possessed by the system in the initial state (or the reactants) would be given out and
the extra energy possessed by the system in the initial state (or the reactants) would be given out and  will be negative.
will be negative.  energy will be absorbed in the process and
energy will be absorbed in the process and  will be positive.
will be positive. Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeCalculate the maximum work obtained when 0.75 mol of an ideal gas expands isothermally and reversibly at 27°C from a volume of 15L to 25L.
If water vapour is assumed to be a perfect gas,
molar enthalpy change for vapourisation of 1 mol of water at 1bar and 100°C is 41kJ mol–1. Calculate the internal energy change, when
(i) 1 mol of water is vaporised at 1 bar pressure and 100°C.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDerive mathematical form of First law of Thermodynamics.
Or
Derive the relationship between heat, internal energy and work.
