 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeCompute internal energy change of a system if it
(i) absorbs 500 kJ heat and does 300 kJ work.
(ii) loses 200 kJ heat and has 450 kJ of work done on it.
A sample of gas is compressed by an average pressure of 0.50 bar so as to decrease its volume from 450 cm3 to 250 cm3. During the process 6.00 J of heat flows out to surroundings. Calculate the change in internal energy of the system.
State whether each of the following will increase or decrease the total energy content of the system:
(i) heat transferred to the surroundings
(ii) work done on the system
(iii) work done by the system.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeEnthalpy: Enthalpy is the total energy associated with the system and is defined as the sum of internal energy and product of its pressure and volume. It is denoted by H.
Mathematically,
H = U + PV
where U is the internal energy change, P and V are respectively the pressure and volume of the system. H is also called heat content of the system. Enthalpy is a state function and every substance has a definite value of enthalpy in a particular state. The absolute value of enthalpy of a substance cannot be determined, but the change in enthalpy (∆ H) accompanying a process can be determined.
Change in enthalpy (∆H): It may be defined as the difference in the enthalpies of the product and reactant species taking part in a chemical reaction at a constant pressure. For example, if HR represents the enthalpies of the reactants and HP represents the enthalpies of the products, then ∆H = Hp – Hr where ∆H gives the change in enthalpy.
The enthalpy change (∆H) is equal to the heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction at constant pressure and constant temperature,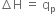
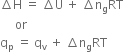
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type