 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeCalculate the heat change accompanying the transformation of C(graphite) to C(diamond). You are given:

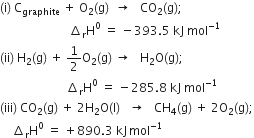
We aim at the equation
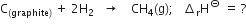
Here we want one mole of C(graphite) as a reactant, so write equation (i) as such. We want two moles of H2(g) as a reactant ; so multiply equation (ii) by 2, we want one mole of CH4(g) as a product, so write equation (iii) as such.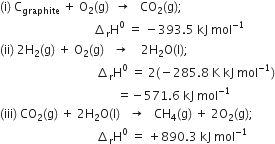
Adding equations (i), (ii) and (iii), we have,
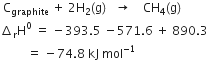
The combustion of one mole of benzne takes place at 298K and 1 atm. After combustion, CO2(g) and H2O (l) are produced and 3267.0 kJ of heat is liberated. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation, ∆fH° of benzene. Standard enthalpies of formation of CO2(g) and H2O(l) are – 393.5 kJ mol–1 and –285.83 kJ mor–1respectively.
What do you mean by bond enthalpy? When is bond enthalpy equal to bond dissociation energy?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type