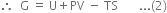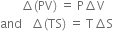Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeProve that in a reversible process:
∆(system) + ∆S(surroundings) = 0
Or
Prove that there is no net change in entropy in a reversible process.
What do you understand by:
(i) The entropy of fusion?
(ii) The entropy of vapourisation ?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeYou are given normal boiling points and standard enthalpies of vapourisation. Calculate the entropy of vapourisation of liquids listed below:
Liquid 

Calculate the entropy change of n-hexane when 1 mole of it evaporates at 341.7 K(∆Hvap = 29.0 kJ mol–1).
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat are the two tendencies which determine the feasibility of process? How are the two related to each other?
What is free energy? Prove that ∆G = ∆H – T∆S.