 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeFind the largest possible area of a right-angled triangle whose hypotenuse is 5 cm long.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeLet AP and BQ be two vertical poles at points A and B, respectively. If AP = 16 m. BQ = 22 m and AB = 20 m, then find the distance of a point R on AB from the point A such that RP2 + RQ2 is minimum.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIf length of three sides of a trapezium other than base are equal to 10 cm. then find the area of the trapezium when it is maximum.
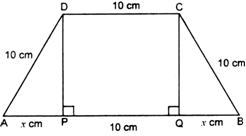
From D, draw DP X ⊥ and from C, draw CQ ⊥ AB
so that PQ = 10 cm.
Now ∆APD ≡ ∆QBC
AP = QB = x cm. say.
In rt. ∠ d ∆APD.
DP2 = AD2 – AP3 = 100 – x2 ⇒ DP =![]()
Also ![]()
Let y be area of trapezium.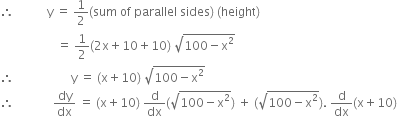
![]()
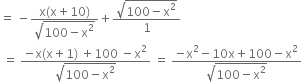
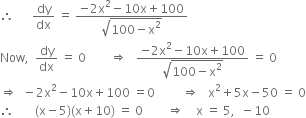
Rejecting x = -10 as distance x cannot be negative, we get, x = 5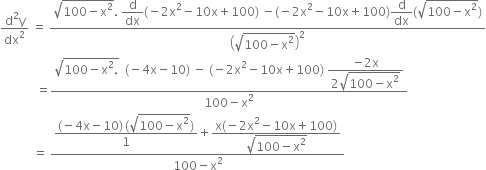
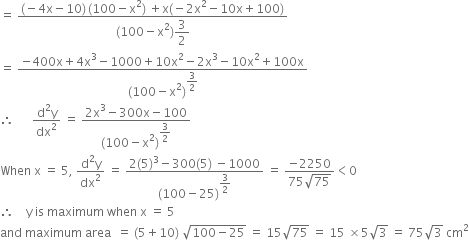
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type