 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeLet r be the radius of the circle whose centre is C and CM ‚ä• x-axis, CN ‚ä• y-axis.
‚ൠ¬Ýcircle touches both the axes
‚ॠ¬Ý ¬Ý CM = CN = r
‚ॠ¬Ý C is (r, r)
‚ॠ¬Ýequation of circle is
(x - r)2¬Ý+ (y ‚Äì r)2¬Ý= r2¬Ý¬Ý¬Ý¬Ý...(1)
Differentiating both sides w.r.t.x,
¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý![]()
or ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý![]()
or ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý![]()
Putting this value of r in (1), we get
¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý¬Ý![]()
or ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý¬Ý![]()
or ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý![]()
or ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý ¬Ý¬Ý![]()
which is the required differential equation.¬Ý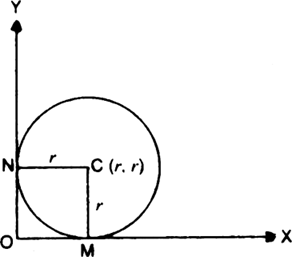
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type