Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type
Given: The side BC of a ∆ABC is produced to D. The bisector of ∠BAC intersects the side BC at E.
To Prove: ∠ABC + ∠ACD = 2 ∠AEC.
Proof: In ∆ABE,
∠AEC = ∠ABC + ∠BAE
| Exterior angle theorem
= ∠ABC + ∠CAE ...(1)
| ∠BAE = ∠CAE (∵ AE bisects ∠BAC)
In ∆AEC,
∠ACD = ∠AEC + ∠CAE
| Exterior angle theorem
⇒ ∠CAE = ∠ACD - ∠AEC ...(2)
From (1) and (2),
∠AEC = ∠ABC + (∠ACD - ∠AEC)
⇒ 2 ∠AEC = ∠ABC + ∠ACD
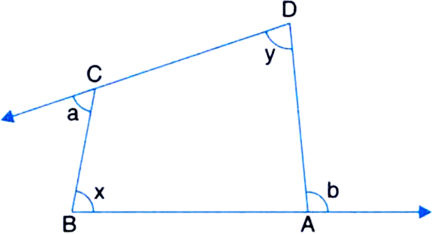
In figure, the sides AB and AC of ∆ABC are produced to points E and D respectively. If bisectors BO and CO of ∠CBE and ∠BCD respectively meet at point O, then prove that ![]()