 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting
(i) an odd number.
(ii) a number greater than 4.
(iii) seven.
A pair of dice is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a total of 5 on two dice.
Two dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that
(i) 5 will not come up on either of them?
(ii) 5 will come up on at least one?
(iii) 5 will come at both dice?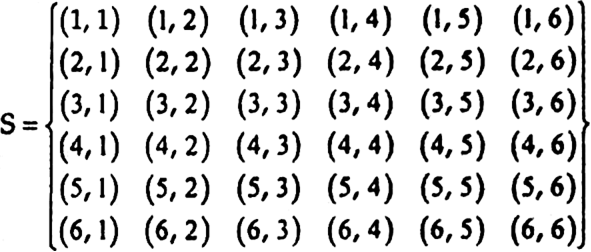
Two dice are thrown simultaneously. Find the probability of getting :
(i) a sum less than 6 (ii) a sum less than 7
(iii) a sum more than 7 (iv) 8 as the sum
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 playing cards. What is the probability that it is
(i) an ace
(ii) a face card
(iii) any card numbered from 2 to 10?
Total number of all possible outcomes = 52
i.e., n( S) = 52
(i) Let E be the favourable outcomes of getting an ace, then
n(E) = 4 Therefore,
P(E) = ![]()
(ii) Let F be the favourable outcomes of getting a face card, then
n(F) = 12 Therefore,
P(F) = ![]()
(iii) Let G be the favourable outcomes of getting any card numbered from 2 to 10, then n(G)= {36}
Therefore,
P(G) = ![]()
One card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards, each of the 52 cards being equally likely to be drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is :
(i) red (ii) either red or king
(iii) red and a king (iv) a red face card
(v) ‘2’ of spades (vi) ‘10’ of a black suit.
