 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeNumber of cards = 52
Number of kings = 5
Number of face cards = 16
Let E denote the event of drawing a king and F the even of drawing face card.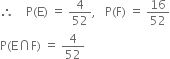
Required probability = P(E/F) = 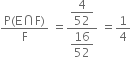
Two coins are tossed once, where
E : tail appears on one coin, F : one coin shows head
Determine P(E | F).
Two coins are tossed once, where
E : no tail appears, F : no head appears
Determine P(E | F).
